A Monohybrid Cross is a cross between two parents that involves only one trait.
For example lets take a cross between a heterozygous mother and father for the height trait.
Tall = T short = t
In the end you would use a punnet square, and cross the genotypes.
You would end up with a 25% chance for a genotype offspring of TT, 50% chance for a genotype offspring of Tt, and 25% chance of a genotype offspring of tt.
You would have 75% chance of having a phenotype/appearance of a tall kid, and 25% for a shortie, like me.
DiHybrid Cross is when you cross two parents and you are mixing two traits.
For example you are mixing a mother who is heterozygous round and heterozygous yellow. (RrYy) and a father who is the same.
R=round seed, r=wrinkled seed, Y= yellow, y= green
First you would have to come up with all possible combinations in the genotypes of each parent.
Eg. RrYy, if you chose two letters at random, could be RY, rY, Ry, or ry.
so you match those 4 options with the 4 you get from the father and you end up with a possibility from 16 offspring.
In this case the resulting genotype ist 9/16 RRYY, 3/16 RRyy, 3/16 rrYY, and 1/16 rryy
for genotype its 9 yellow round, 3 green round, 3 wrnikled yellow, and 1 wrinkled green.
Thats Monohybrid and DiHibrid Crossing.
Sunday, December 15, 2013
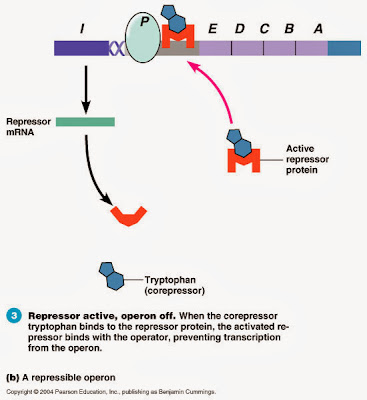
Operon System
DNA Reptile. (Replication)
DNA replication is a process where DNA replicates itself.
There are many enzymes that help in this process.
Helicase- The scissors in the group.
Starting from the Origin of Replication (the starting point) Helicase, (In class we used a yellow triangle to represent Helicase. You can do this if you need some visual aids) breaks down the Hydrogen bonds that connect the two bases.
It does this to unwind the double helix, and prepare a single stranded DNA replication.
There are many enzymes that help in this process.
Helicase- The scissors in the group.
Starting from the Origin of Replication (the starting point) Helicase, (In class we used a yellow triangle to represent Helicase. You can do this if you need some visual aids) breaks down the Hydrogen bonds that connect the two bases.
It does this to unwind the double helix, and prepare a single stranded DNA replication.
Then RNA primase comes on and places rna pairings to the single stranded dna. For example, if you had a strand that read CTAG, the RNA paired with it would be, GAUC, with the Thymine being replaced with Uracil.
It does this to allow DNA Polymerse III the ability to read the strands, because it places rna which has a 3' OH base, which DNA polymerse III can read.
DNA polymerse III then comes in and reads the strand of RNA and creates the complementary nucleotides. Each new base forms phosphodeister bonds.
DNA Polymerse I then replaces the rna with the newly created bases.
Ligase glues all the okazaki fragments together.
DNA Structure
According to Wikipedia, Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
Basically, DNA is our human code. It makes us, us. Every cell in our body has the same DNA in it.
DNA is usually in a shape of a double helix, and has two strands running in opposite directions. (5' - 3', and 3' - 5')
There are 4 bases, Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine. A goes with T and G goes with C to form base pairs. Each base is connected to the sugar phosphate backbone.
Basically, DNA is our human code. It makes us, us. Every cell in our body has the same DNA in it.
DNA is usually in a shape of a double helix, and has two strands running in opposite directions. (5' - 3', and 3' - 5')
There are 4 bases, Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine. A goes with T and G goes with C to form base pairs. Each base is connected to the sugar phosphate backbone.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
.jpg)